-
Products
- Products Top
- New Products Infomation
- Selection Guide
- Product Catalogue
- Product Category
- Global Network
-
Technical
Information- Technical Information Top
-
How to use chip resistors smartly
- 1.Basic knowledge of resistors
- 2.Manufacturing methods and characteristics of thin film resistors
- 3.Performance characteristics of thin film resistors
- 4.High precision and high reliability
- 5.Trimmable chip resistors and altering resistive values
- 6.Application and recommended usage of thin film chip resistors
- 7.Application and recommended usage of small high power thin film ship resistors
- 8.Various methods of current sensing and advantage of current sensing resistors
- 9.Application and recommended usage of current sensing resistors
- Smart usage of High Frequency Chip Components
- Application Information
-
Product Technical Report
Standard Specification for surface mount chip resistors
- Recommended land patterns
- Recommended reflow and flow soldering profile
- Dimensions of the packaging reel
- Dimensions of the packaging tape
Standard Specification for High frequency surface mount components
- Recommended reflow soldering profile
- Dimensions of the packaging tape
- Dimensions of the packaging reel
-
Technical FAQ
High Precision Thin Film Chip Resistors
- ・Part numbering
- ・Performance characteristics
- ・Quality, reliability
- ・Mounting, packaging
Current sensing chip resistors
- ・Part numbering
- ・Performance characteristics
- ・Quality, reliability
- ・Mounting, packaging
- Company Profile
-
QC and Environmental
Activities
- HOME
- Technical Information
- 1.Basic knowledge of resistors
1.Basic knowledge of resistors
1.1 Resistors and Ohm’s law (how resistors function in circuits)
Typical passive components
- ・Resistors
- ・Capacitors
- ・Inductors (coils)
Ohm’s law is applicable to resistors
Possible usage of resistors under Ohm’s law.
- ・Deciding voltage
- ・Deciding current
- ・Measuring current
- ・Consuming power(converting electricity to heat)

Series or parallel resistors and voltage
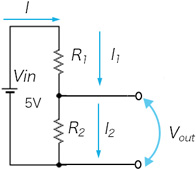
Vout = R2/(R1+R2)
I= Vin/(R1+R2)
I= I1= I2
In series, voltage is proportional to the resistance
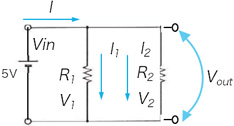
I= I1+ I2
Vout= V2 = V1 = Vin
R1:R2=I2: I1
In parallel, voltage is the same on each resistors
Current is negatively proportional to resistance
1.2 Resistor marking and E series
The resistive value is expressed in 3 or 4 digit numbers following E-series. E-series are geometric progression series and depending on how many numbers used between 1 and 10, they are called E12, E24, and E96 series.
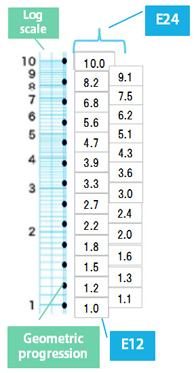
E12 series is a geometric progression
1210n Substitute “n”with 0…11, and you get
1.0, 1.2, 1.5, … 8.2,
12 values with same ratio.
E24 series adds a number in between each of the E12 series, making them 24 numbers. 2410n

Resistance value is expressed in 3 or 4 digit alpha numeric number on top of the products unless the surface is too small to mark.
⇒Significant figures are expressed in E series.
Additional explanation:Examples of resistance value expression
Chip resistors currently ranges from mΩ(milliohms)to MΩ(mega Ohms). Using the power of 10 and E series, resistance value is expressed as follows. The number of digits changes depending on the size and resistance value(For details, refer to the each product series. E-series are described on page 7 of the catalogue. )
Resistance value range and units

E6, E12, E24 series has 2 significant figures
Last digit is n of 10n
n=1 ⇒101= 10
n=2 ⇒102= 100
n=3 ⇒103= 1000
R means decimal point under 10Ω
E96 series has 3 significant figures
Last digit is n of 10n
n=1 ⇒101= 10
n=2 ⇒102= 100
n=3 ⇒103= 1000
Under 1Ω, numbers after decimal point is expressed in 3 digits after R
3 digit designation
102=> 10 x 100 = 1kΩ
331=> 33 x 10 = 330Ω
3R0=> 3.0 Ω
*Refer to page 7 of the catalogue for 3 digits expression of E96 series
4 digit designation
1002=> 100 x 100 = 10kΩ
4990=> 499 x 1 = 499Ω
3303=> 330 x 1000= 330kΩ
3R00=> 3.0Ω
R220=> 0.22Ω =220mΩ
R005=> 0.005Ω = 5mΩ
Technical Information
-
- 1.Basic knowledge of resistors
- 2.Manufacturing methods and characteristics of thin film resistors
- 3.Performance characteristics of thin film resistors
- 4.High precision and high reliability
- 5.Trimmable chip resistors and altering resistive values
- 6.Application and recommended usage of thin film chip resistors
- 7.Application and recommended usage of small high power thin film ship resistors
- 8.Various methods of current sensing and advantage of current sensing resistors
- 9.Application and recommended usage of current sensing resistors
-
-
Standard Specification for surface mount chip resistors
- Recommended land patterns (soldering footprints)
- Recommended reflow and flow soldering profile
- Dimensions of the packaging reel
- Dimensions of the packaging tape
-
Standard Specification for surface mount chip resistors
-
- High Precision Thin Film Chip Resistors Current sensing chip resistors
Please feel free to contact us about products,
requesting documents and samples.
Activity Contents
Technical Information
How to use chip resistors smartly
- 1.Basic knowledge of resistors
- 2.Manufacturing methods and characteristics of thin film resistors
- 3.Performance characteristics of thin film resistors
- 4.High precision and high reliability
- 5.Trimmable chip resistors and altering resistive values
- 6.Application and recommended usage of thin film chip resistors
- 7.Application and recommended usage of small high power thin film ship resistors
Standard Specification for surface mount chip resistors
- Recommended land patterns
- Recommended reflow and flow soldering profile
- Dimensions of the packaging reel
- Dimensions of the packaging tape
Standard Specification for High frequency surface mount components
Smart usage of High Frequency Chip Components
Susumu Deutschland GmbH

